How Remote Health Monitoring Is Revolutionizing Healthcare Delivery?
Remote health monitoring is one of the most groundbreaking advancements in the healthcare industry today. By leveraging technology, healthcare providers can track a patient’s health status in real-time without the need for in-person visits. This form of monitoring allows patients to remain in the comfort of their homes while still receiving the necessary care and attention from healthcare professionals. Remote health monitoring (RHM) has proven particularly beneficial for managing chronic conditions, improving patient engagement, reducing healthcare costs, and enhancing overall healthcare delivery. Let’s explore how this innovative approach is revolutionizing healthcare delivery.
Key Takeaways
- Continuous Monitoring for Chronic Diseases: RHM provides ongoing monitoring for chronic conditions, enabling early detection and timely intervention.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: Patients can track their own health metrics, leading to greater involvement in their care.
- Cost Reduction: RHM reduces the need for frequent in-person visits, lowering healthcare costs for both patients and providers.
- Better Coordination of Care: Real-time data sharing between healthcare providers leads to improved collaboration and more coordinated care plans.
- Improved Access to Healthcare: Remote health monitoring expands access to care for individuals in rural or underserved areas.
What Is Remote Health Monitoring?
Remote health monitoring (RHM) refers to the use of digital tools and technologies to track, record, and manage a patient’s health data in real-time. This can include devices such as wearable health trackers, smartwatches, and mobile applications that continuously collect vital health data like blood pressure, heart rate, glucose levels, oxygen saturation, and even sleep patterns. The collected data is sent to healthcare professionals, who can then analyze it remotely and make adjustments to treatment plans as necessary. RHM can be used for a variety of health conditions, including chronic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and respiratory conditions. It also serves as a preventative measure for those at risk of developing health issues by allowing early intervention based on the data received.
How Remote Health Monitoring Enhances Healthcare Delivery
- Continuous Monitoring for Chronic Disease Management
One of the primary advantages of remote health monitoring is its ability to provide continuous monitoring for patients with chronic conditions. Managing chronic diseases often requires frequent check-ups and monitoring of various health metrics, which can be time-consuming and costly for both patients and healthcare providers. Remote health monitoring allows healthcare providers to track patients’ conditions in real-time, making it easier to detect any fluctuations or abnormalities before they become serious issues. For instance, patients with diabetes can wear a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) that tracks their blood sugar levels throughout the day. If a significant deviation from the patient’s normal range occurs, healthcare providers are notified and can take immediate action, reducing the risk of complications like diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia. - Early Detection and Prevention
Remote monitoring plays a critical role in the early detection of health problems. For example, patients who use wearable heart monitors can track irregularities in their heart rate or rhythm, alerting their healthcare providers to potential conditions such as arrhythmias or cardiovascular diseases. Similarly, patients with hypertension can monitor their blood pressure at home using connected devices, ensuring that any dangerous spikes are detected early, leading to more effective prevention and treatment. Early detection allows for proactive management, often preventing more serious health conditions from developing or worsening. It also helps reduce the burden on emergency services and the overall healthcare system by catching health issues before they require hospitalization or urgent care. - Improved Patient Engagement and Empowerment
Remote health monitoring empowers patients to take a more active role in managing their own health. With the ability to track their own health data in real time, patients can become more aware of their conditions and understand how their lifestyle choices impact their health. This transparency promotes greater accountability, encourages healthy habits, and motivates patients to follow prescribed treatment plans. For example, a person with hypertension who is monitoring their blood pressure may be more likely to take medications as prescribed, make dietary changes, or increase their physical activity to keep their readings within a healthy range. The sense of ownership over one’s health fosters improved adherence to treatment plans and ultimately leads to better health outcomes. - Reduced Hospital Visits and Healthcare Costs
Traditional healthcare often requires patients to visit clinics or hospitals regularly for check-ups, which can be expensive and time-consuming, especially for those with chronic conditions. Remote health monitoring reduces the need for in-person visits, allowing patients to have more frequent and efficient check-ups without leaving their homes. By cutting down on hospital admissions and emergency room visits, RHM helps reduce the strain on healthcare facilities and lowers overall healthcare costs. It also allows healthcare providers to manage a larger number of patients without compromising the quality of care. Remote health monitoring tools can send updates on the patient’s condition, providing healthcare professionals with enough data to make informed decisions, thus reducing unnecessary visits. - Enhanced Coordination Between Healthcare Providers
Remote health monitoring systems facilitate improved communication between healthcare providers and specialists. For patients with complex health issues requiring input from multiple specialists, remote monitoring ensures that all relevant providers have access to the same up-to-date data. This seamless exchange of information helps create more coordinated care plans and ensures that patients receive consistent care, no matter how many providers are involved. For instance, a patient with both diabetes and heart disease can have their blood glucose levels monitored by an endocrinologist while their heart rate and blood pressure are tracked by a cardiologist. This integrated care approach improves patient outcomes, as providers can work together to adjust treatments based on comprehensive health data. - Convenience and Accessibility for Patients
For patients, particularly those living in rural areas or with limited access to healthcare facilities, remote health monitoring offers an unprecedented level of convenience. They no longer need to travel long distances to receive healthcare services or wait for months to see specialists. With remote monitoring tools, patients can receive high-quality care in the comfort of their homes. Telemedicine platforms that integrate remote health monitoring also allow patients to have virtual consultations with healthcare providers. This means that healthcare services are accessible even to those who may have mobility issues or live in remote regions, eliminating barriers to healthcare access.
How Remote Health Monitoring Improves the Management of Specific Conditions
- Diabetes
Patients with diabetes benefit immensely from remote health monitoring. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) devices are increasingly common and allow individuals with diabetes to keep track of their blood sugar levels in real-time. This data is shared with healthcare professionals, who can adjust medications or provide lifestyle recommendations to help manage the condition. The ability to quickly respond to fluctuations in blood glucose levels reduces the risk of long-term complications, such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems. - Hypertension
Hypertension is a common and often silent condition that can lead to severe health issues like heart attack, stroke, or kidney damage. Remote monitoring of blood pressure allows patients to track their readings throughout the day, providing valuable data for healthcare providers. If a patient’s blood pressure reaches dangerous levels, providers can adjust medication or suggest lifestyle changes to prevent a crisis. - Heart Conditions
Remote health monitoring is particularly beneficial for patients with heart conditions, such as arrhythmia or congestive heart failure. Wearable heart monitors track the electrical activity of the heart, allowing healthcare providers to detect irregularities in real-time. If an abnormal heart rhythm is detected, healthcare providers can recommend timely interventions, such as changes to medications or the need for further tests. This ability to monitor the heart continuously allows for better prevention of cardiac events. - Respiratory Conditions
For individuals with respiratory diseases like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), remote health monitoring tools can track symptoms such as lung function and oxygen saturation levels. If a patient experiences a drop in oxygen levels, healthcare providers can respond quickly, preventing more severe complications. In addition, respiratory monitoring devices allow for better management of inhaler use, ensuring that patients follow their prescribed treatment regimens.
Challenges and Considerations of Remote Health Monitoring

While remote health monitoring offers tremendous benefits, there are challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its widespread success.
- Data Privacy and Security
With the increase in remote data collection, there are concerns over the privacy and security of patient data. Ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) and implementing strong encryption protocols are essential to protecting patient information and maintaining trust in remote health monitoring systems. - Technology Access and Literacy
Not all patients have access to the technology required for remote health monitoring, such as smartphones, wearables, or reliable internet connections. Additionally, some patients, especially older adults, may lack the technical literacy needed to use these devices effectively. Ensuring equitable access to technology and providing patient education are crucial in overcoming these barriers. - Reliability and Accuracy of Devices
Remote monitoring devices must be accurate and reliable for healthcare providers to make informed decisions. There are concerns about the potential for faulty readings or device malfunctions, which could result in misdiagnoses or inappropriate treatment plans. Manufacturers must ensure that devices meet rigorous standards for accuracy and reliability.
Further Advancements in Remote Health Monitoring Technology
While remote health monitoring has already brought about substantial benefits, the technology continues to evolve rapidly. Innovations in sensors, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and data analytics are poised to revolutionize the space even further. As these technologies progress, the accuracy, convenience, and effectiveness of remote health monitoring will continue to improve.
1. Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI has the potential to significantly enhance the capabilities of remote health monitoring systems. Machine learning algorithms can process the vast amounts of data generated by wearable devices and predict potential health issues before they become critical. For example, AI-powered systems can analyze patterns in a patient’s vital signs and identify early warning signs of heart attacks, strokes, or seizures. These predictive capabilities can be integrated into remote health monitoring tools to alert healthcare providers before a medical emergency occurs, giving patients a better chance of recovery.
AI can also help healthcare professionals by providing real-time analysis of data, allowing them to make quicker and more accurate decisions. These AI systems can continuously improve through machine learning, learning from past patient data to refine their predictions and recommendations.
2. Enhanced Wearable Devices
Wearable technology continues to improve, with new sensors and designs being developed to monitor a broader range of health metrics. For instance, current smartwatches are capable of measuring heart rate, ECG, oxygen levels, and even detecting falls. However, the future of wearable health devices is even more promising. Newer devices may be able to measure additional health parameters, such as blood glucose levels, hydration levels, or even neurotransmitter levels for mental health monitoring.
As wearables become more sophisticated, they will not only monitor vital signs but also offer more detailed insights into overall health and wellness, supporting preventive healthcare in a more holistic way.
3. Virtual Reality and Remote Health Education
Virtual reality (VR) is another area where remote health monitoring could evolve. VR has already been integrated into rehabilitation programs, helping patients recover from physical injuries. In the future, VR could be used for mental health care as well, offering virtual therapy sessions and relaxation techniques to manage stress, anxiety, and other psychological conditions.
Moreover, healthcare education can also be improved through VR. For instance, remote consultations could be paired with VR simulations that help healthcare providers assess a patient’s condition and provide more personalized advice.
The Future of Remote Health Monitoring in Developing Countries
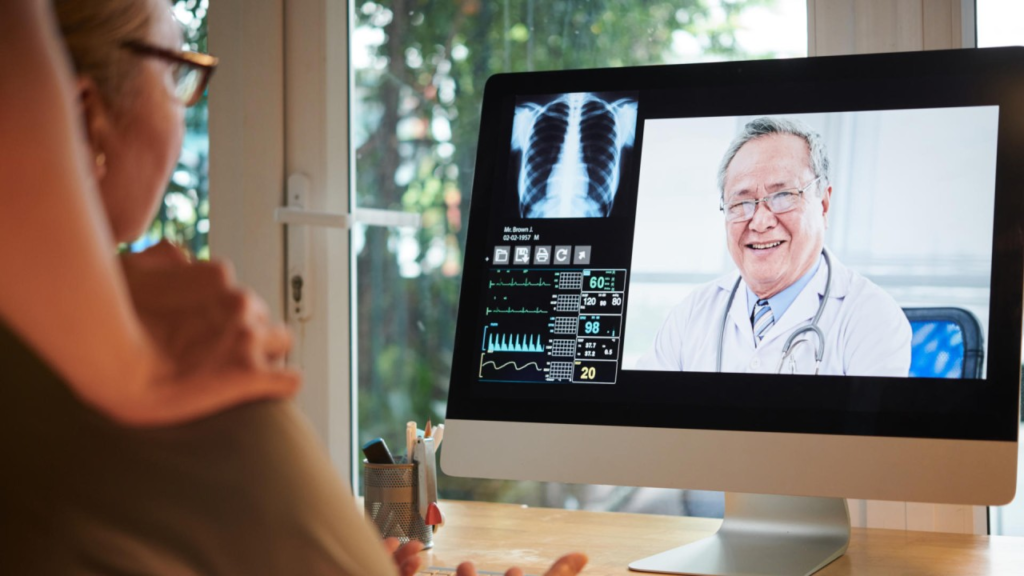
While remote health monitoring is making great strides in developed countries, it also holds significant potential for transforming healthcare in developing nations. These countries often struggle with limited access to healthcare professionals, inadequate infrastructure, and financial constraints. Remote health monitoring could alleviate some of these challenges by providing a scalable and cost-effective way to deliver healthcare services.
In regions where access to healthcare facilities is limited, remote monitoring can enable individuals to track their health from home, receive regular check-ups, and consult with doctors remotely. This would significantly reduce the need for patients to travel long distances to receive care, making healthcare services more accessible, affordable, and timely.
Additionally, remote health monitoring could help in emergency situations where immediate medical attention is needed but local healthcare resources are scarce. For instance, a wearable device that tracks a patient’s vital signs could be connected to a central system that alerts healthcare providers to potential crises, such as heart attacks or strokes. With timely intervention, lives could be saved, and outcomes could be drastically improved in regions where healthcare resources are limited.
The Role of Remote Health Monitoring in Post-Pandemic Healthcare Systems
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of remote healthcare solutions, including remote health monitoring. With social distancing measures and restrictions on in-person visits, many healthcare systems had to adapt to the increasing demand for telemedicine and remote patient care. As we move into a post-pandemic world, remote health monitoring will continue to play a crucial role in shaping healthcare systems around the globe.
The pandemic made it clear that healthcare systems need to be flexible and resilient to future global challenges. Remote health monitoring provides a solution to improve patient care while minimizing the spread of infectious diseases. Even in non-pandemic times, remote health monitoring can enhance routine care, reduce waiting times, and provide patients with timely and convenient healthcare services.
Moreover, the post-pandemic landscape will likely see an increased demand for hybrid care models, where patients receive a combination of virtual and in-person consultations. Remote health monitoring will be central to this hybrid model, allowing healthcare providers to continuously track patients’ health data and offer ongoing support without requiring frequent in-person visits.
Remote Health Monitoring and Mental Health
While much of the discussion around remote health monitoring has focused on physical health, its impact on mental health is equally significant. The ability to remotely monitor and intervene in mental health conditions could be a game-changer for individuals who struggle with anxiety, depression, or other mental health disorders.
With remote health monitoring, wearable devices could track behavioral patterns, sleep quality, and stress levels, providing healthcare providers with a broader picture of a patient’s mental health. This data could be used to assess symptoms, detect early warning signs of mental health crises, and ensure timely intervention.
For example, a wearable device that monitors sleep quality could alert a mental health professional if a patient is experiencing disrupted sleep patterns, which are often linked to anxiety or depression. Similarly, monitoring a patient’s heart rate variability could provide insights into their emotional state, enabling healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans and offer personalized care.
Remote Health Monitoring in the Elderly Population
The elderly population often faces unique health challenges, including chronic conditions, cognitive decline, and mobility issues. Remote health monitoring can have a profound impact on their quality of life by offering an effective way to manage and monitor these health concerns without the need for constant in-person visits to healthcare facilities.
1. Monitoring Chronic Conditions
Older adults are often at risk for conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease. Remote health monitoring tools allow healthcare professionals to track their patients’ vital signs remotely, providing real-time data that can be used to make timely decisions regarding medication adjustments or lifestyle changes. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches or continuous glucose monitors (CGM), can help elderly individuals monitor conditions like diabetes or heart disease, ensuring that they stay within healthy ranges and prevent complications.
2. Preventing Falls and Monitoring Mobility

Falls are a leading cause of injury and hospitalization among the elderly. Remote health monitoring devices that include motion sensors and accelerometers can detect falls in real time and immediately alert caregivers or healthcare providers. This feature reduces the time it takes to get help after an elderly person falls, which can often be a matter of life or death. Additionally, wearable devices can monitor physical activity levels and provide insights into the patient’s mobility. This allows for early intervention in case of a decline in physical function, which is important for maintaining independence and preventing further health complications.
3. Cognitive Health Monitoring
Cognitive decline, including conditions like dementia and Alzheimer’s disease, is another significant concern for the elderly population. Remote health monitoring can track behavioral patterns, activity levels, and sleep patterns that are indicative of cognitive health. Some remote devices can use voice recognition to monitor for signs of confusion or memory loss, alerting healthcare providers when changes are detected. Early intervention can be critical in delaying the progression of cognitive decline and improving the patient’s overall quality of life.
4. Medication Adherence
Medication management is another challenge faced by older adults. Many elderly individuals struggle with managing multiple medications, which can lead to errors in dosing or missed doses. Remote monitoring tools can help track medication adherence, sending reminders to the patient when it’s time to take their medication. Some advanced systems can even alert caregivers or family members if a dose is missed, ensuring that patients are receiving the treatment they need.
Also Read: How Does Telemedicine Online Healthcare Enhance Healthcare Services?
Conclusion
Remote health monitoring is fundamentally changing the way healthcare is delivered. By enabling continuous tracking of health metrics, RHM empowers both patients and healthcare providers to make informed, real-time decisions about care. This leads to better management of chronic conditions, enhanced patient engagement, and reduced healthcare costs. With technological advancements and increased accessibility, remote health monitoring is set to become an integral component of modern healthcare, benefiting both patients and healthcare systems alike. The future of remote health monitoring holds even more promise, with the potential for further innovations in wearable technology, artificial intelligence, and data analytics that will enhance patient outcomes and transform healthcare delivery for the better.
FAQs
1. What is remote health monitoring?
Remote health monitoring uses technology, like wearables and apps, to track a patient’s health data in real time, allowing healthcare providers to manage care remotely.
2. How does remote health monitoring improve patient care?
It allows for continuous monitoring, early detection of health issues, and proactive interventions, leading to better outcomes and fewer hospital visits.
3. What devices are used for remote health monitoring?
Wearables, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, along with specialized devices like blood pressure cuffs and glucose monitors, are commonly used.
4. Is remote health monitoring safe?
Yes, it’s safe, as long as devices are FDA-approved and data is securely encrypted to protect patient privacy.
5. Can remote health monitoring replace doctor visits?
It reduces the need for visits but doesn’t fully replace them. It works alongside in-person visits for ongoing care and routine check-ups.
6. Who benefits from remote health monitoring?
Patients with chronic conditions, the elderly, and those in remote areas all benefit from convenient, ongoing care without frequent hospital visits.
7. How does remote health monitoring save money?
It cuts costs by preventing hospital readmissions, reducing emergency visits, and promoting early interventions, leading to lower treatment costs.
